What are Case Statements in SQL
Case statements are a very powerful tool for an analyst
Allowing you to add your own dynamic data classification, cleanse and structure data
In SQL, CASE statements allow you to check for various conditions and return a value if a condition is met.
CASE statements always begin with the CASE keyword and end with the END keyword.
A little bit like having multiple, nested IF statements
If no conditions are true a default value can be used to always return a last resort value
CASE statement syntax and example
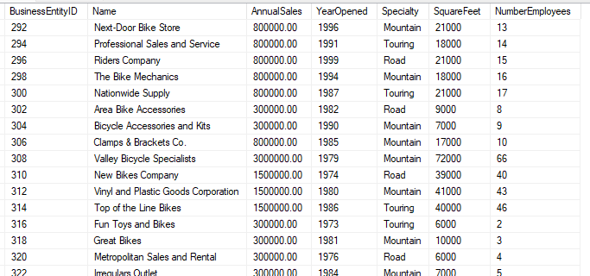
Assume we have a list of retail stores of various sizes, but we want to grade them based on their sizes
Rules
Large = greater than 50,000 sqft
Medium = 25,000 to 50,000 sqft
Small = less than 25,000 sqft
From this data, we will apply this case statement
SELECT Name, squarefeet
, case
when squarefeet < 25000 then ‘Small’
when squarefeet < 50000 then ‘Medium’
else ‘Large’ end as [Store Size Grade]
FROM [AdventureWorks2019].[Sales].[vStoreWithDemographics]
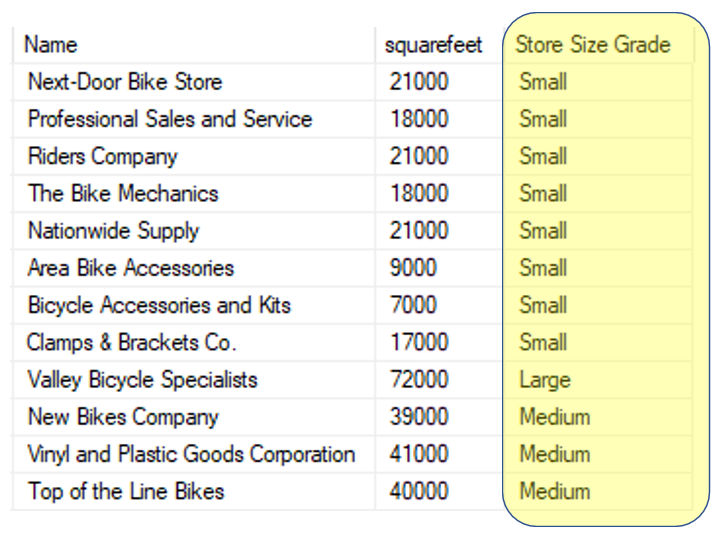
Running this gives us
case
when squarefeet < 25000 then ‘Small’
when squarefeet < 50000 then ‘Medium’
else ‘Large’
end as [Store Size Grade]
Key points to note
It is often easier to read if the rules (the rows beginning ‘when’) are on a separate row and indented
The case statement applies the first rule that is satisfied in the order they appear
Note the final ‘Large’ rule doesn’t need a greater than 50,000 rule, because it is the remaining records, making it easier to read
You are not limited to setting rules against a single column
you could use a combination of columns, or even nest a case statement within a case statement like this example
Typical uses for the CASE statement
The SQL CASE statement can be used within other types of statement such as SELECT, UPDATE, DELETE and SET, and in clauses such as IN, WHERE, ORDER BY, and HAVING.
Here are some other use cases for the SQL CASE statement:
- Checking for the presence or absence of a value e.g. PASS / FAIL grades for data quality
- Prevention of divide by zero errors in calculations
- Creating groupings and binning
- Splitting values into separate columns
The CASE statement in SQL can be put to use in many powerful ways
creating useful groupings, calculating outputs based on a number of variables, transforming data, transposing data
Getting started is easy and with some imagination and practice you will no doubt find CASE statements to be one of the most powerful and flexible tools in your SQL toolbox
Subscribe to our channel to see more tips and timesavers
Select Distinct YouTube Channel
Or find other useful SQL, Power BI or other business analytics timesavers in our Blog
Our Business Analytics Timesavers are selected from our day to day analytics consultancy work. They are the everyday things we see that really help analysts, SQL developers, BI Developers and many more people.
Our blog has something for everyone, from tips for improving your SQL skills to posts about BI tools and techniques. We hope that you find these helpful!



